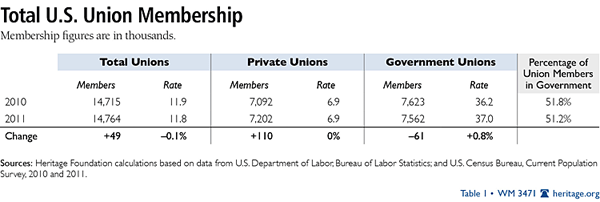
Union density in the American workplace fell to a new post–World War II low of 11.8 percent in 2011. Private-sector union membership remained at 6.9 percent—less than when President Franklin Roosevelt signed the National Labor Relations Act (NLRA).
Union membership has fallen because traditional collective bargaining does not appeal to most workers. Polls show that only one in 10 non-union workers wants to organize. This makes sense: In the competitive private sector, unions can do little to raise their members’ pay. Additionally, most workers like their jobs and believe they are on the same side as their employers.
But while workers reject unions, they do want a voice in the workplace. Unfortunately, the NLRA prohibits employee–employer working groups that give employees that voice. It is time for Congress to allow non-union employers and employees to work together to improve working conditions.
Falling Union Membership
The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that union membership continues to stagnate. While employers added 1.6 million net new jobs in 2011, union membership increased by only 49,000 net workers. As a result, union density fell 0.1 points to a new postwar low of 11.8 percent.

Private-sector unionization rates held steady at 6.9 percent, while government unionization increased 0.8 points to 37 percent. Total union density fell because state and local governments cut spending to balance their budgets. So while employment grew (+1.9 million) in the largely non-union private sector, it shrank (-300,000) in the government.[1] Since the government is much more heavily unionized than the private sector, this caused union density to fall.
A majority of union members (51.2 percent) work in government. More than twice as many union members now work in the U.S. Postal Service as in the domestic auto industry.[2] This represents a significant historical reversal. President Roosevelt opposed the idea of unions in government.[3] George Meany, the first president of the AFL-CIO, famously stated that “It is impossible to bargain collectively with government.”[4] Now the size of the union movement moves in tandem with the size of government.
Unions Do Little for Private-Sector Workers
Why are so few private-sector workers union members? Because most workers do not want to unionize. Polling shows that only 9 percent of non-union employees want to join a union, while 81 percent do not.[5] This low support makes organizing new companies difficult. The United Auto Workers (UAW), for example, has repeatedly failed to organize the employees of foreign automakers. Unions are not recruiting enough new members in the private sector to replace those they lose when unionized firms go bankrupt.
The fact that employees do not want to join a union should not be surprising. Changes in the economy and the workplace have made unions less attractive.
Private-Sector Unions Do Not Raise Wages
Private-sector unions now have little power to raise their members’ wages. Deregulation and free trade have made the economy more competitive. Consequently, unionized companies cannot pass higher labor costs on to consumers.[6] If they raise their prices, consumers will take their business elsewhere.
Unions recognize this and do not want to lose their dues-paying members. As UAW President Bob King recently put it: “If we go in, we dramatically raise fixed costs for Ford, General Motors or Chrysler, we’re shooting ourselves in the foot.…We don’t want to disadvantage the [unionized auto] companies.”[7]
As a result, unions do not negotiate higher pay. Research shows that private-sector workers who vote to join a union earn no more than workers who vote against unionizing.[8] This removes much of the incentive to organize and pay union dues. Unions remain strong only in the government—the one sector of the economy that faces no competition.
Workers Satisfied with Their Jobs
Employers have also learned that respecting their employees makes business sense. Modern human resource management practices treat employees as a valuable resource. As a result, overwhelming majorities of employees say that they are satisfied with their jobs and like their supervisors. Very few workers feel they need protection from an abusive employer.

Instead, most workers believe they and their employers are on the same side. Employees want to work cooperatively with management.[9] Most workers have no interest in unionizing against their companies.
This does not mean that employees do not want a voice in the workplace. Surveys show that workers want to participate in workplace decisions and want to be heard by their supervisors. What they want to avoid is conflict with management.[10]
Employees Do Want Participation
Many employees (and employers) would like employee involvement (EI) programs and work groups in which workers and supervisors can meet to discuss workplace issues. These programs can take many forms. Examples include self-directed work teams, safety committees, and production committees.[11] The essential element is advancing employee interests through employee involvement. Polls show that 60 percent of workers prefer EI programs to improve working conditions over either more government regulations or labor unions.[12] Examples of effective EI programs that advance worker interests abound. For instance:
- Webcor Packaging, Inc., a manufacturing company in Flint, Michigan, formed a plant council consisting of five elected employees and three appointed managers to pursue ways to improve work rules, wages, and benefits. The council members took suggestions from all employees and made recommendations to management based on those suggestions.
- Employees at Electromation, Inc., in Elkhart, Indiana, opposed a plan to change the attendance bonus the company offered. In response, the company met with randomly selected employees and formed action committees to solve various workplace problems. The company asked committee members to meet with other workers and promised to implement the solutions if they were not cost-prohibitive.[13]
Law Prohibits Most Employee Involvement Programs
These EI programs gave workers a say in the workplace and improved working conditions. They were also illegal.
The government forced Webcor and Electromation to disband their EI programs.[14] Section 8(a)(2) of the NLRA prohibits employer-dominated “labor organizations.” This outlaws virtually any work council or EI program that gives workers a real voice in the workplace. Any form of two-way discussions between workers and management over working conditions outside of collective bargaining violates the law.
Choice and Voice in the Workplace
Congress passed this ban to prevent companies from creating and negotiating with employer-dominated “company unions” to fight off organizing drives. This has become an anachronism. Few workers now want to unionize in any event. Companies today create EI programs to improve working conditions, helping them attract and retain valuable employees.
The law should encourage employers to do so. Cooperative workplace programs would allow employers and employees to innovate and adapt workplace relations to the modern economy. By an 85 percent to 10 percent margin, workers say they prefer employee organizations run by employees and management together to organizations run by employees alone.[15] Congress should give employees that choice.
James Sherk is Senior Policy Analyst in Labor Economics in the Center for Data Analysis at The Heritage Foundation.